Open the world of Blockchain development - Chapter 5: Trustless (consensus)
Can you completely trust someone even though they are with you? Want but cannot, right? We are living in the world that most of situation is grey color, anyone or anything is your comrade today may turn in to your enemy tomorrow. Blockchain is a large system which was built by the community, how to make sure the last information set in Block is the truth?
Byzantine fault tolerance
This is a traditional topic to check if a server can be inconsistently. In its simplest form, a number of generals are attacking a fortress and they must decide as a group whether to attack or retreat. Some generals may prefer to attack, while others prefer to retreat. The important thing is that all generals agree on a common decision, for a halfhearted attack by a few generals would become a Rout, and would be worse than either a coordinated attack or a coordinated retreat.

In computer science field, we will make an election by using ECC to make unique signed vote of each general that can be easy verify (hard to fake).
The strategy is: First, we need to choose a decision is attack or retreat. For example, we would choose attack, then make an election with other generals. If number of votes that have same result as attack more than 2/3+1 vote, then attack is a final decision. Otherwise, the election is stuck there so they will do nothing and continue the siege.
The proof
Beside of BFT, we have others mechanism to keep the network trustless. They are Proof of work (Bitcoin, 1st Blockchain generation), Proof of stake (Ethereum, 2nd generation), Delegated proof of stake (EOS, 3rd generation) and Proof of history (Solana).
Proof of work
Blockchain’s most known consensus is Proof of Work. An overview of how it works in the image below:
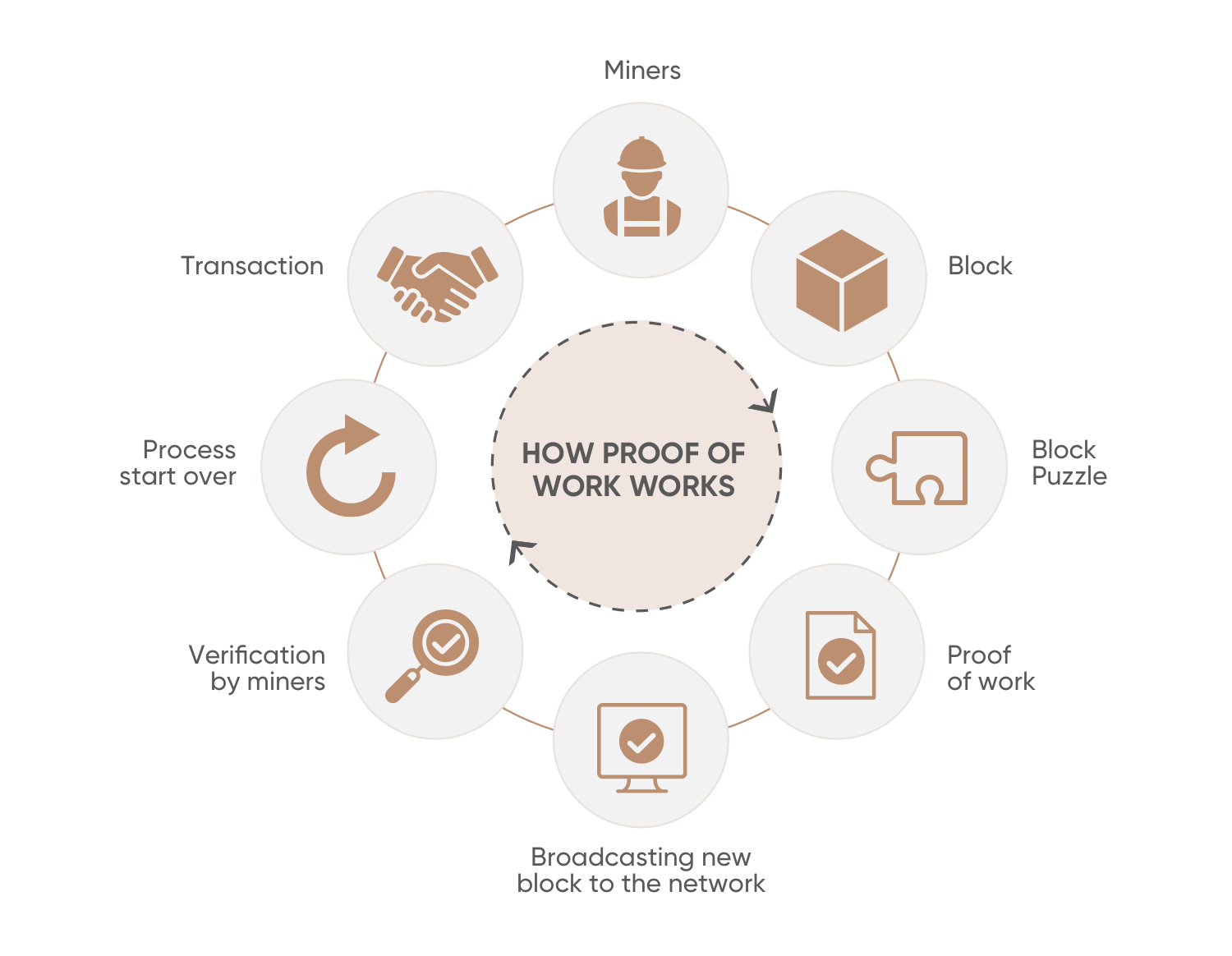
The unique of PoW is miners need computer calculator power to find a hash for closing Block as soon as possible. This is requirement to have Block reward and transaction fee of that Block, complexity of find nonce to close Block hash has been updated once each two weeks to make sure miners sill took time to verify Block be close with block time.
The different thing with BFT is transaction only need 51% of approved network power to mark as success, if any Block that does not follow mechanism of Blockchain, they will be fork to another Blockchain. So, this solution problem is be forked many times because it is not okay with fault node within.
Proof of stake
Because required much power on calculating the nonce to close the Block, PoW be criticism because of power washing or non-environment friendly. Proof of Stake or PoS is a solution for this problem.

The main different between PoW and PoS is miner now need to stake their native token to have chance to be selected as Block’s validator to get Block reward and transaction fees of that Block.
Now the game is changed, instead of calculating power race now become staking power race so it still keeps the network safe as PoW and now reduce the cost of maintain network, is it? Not really, because of not requiring calculating power mean less people willing to run a Node. But we still have tradeoff for this problem is the network can be smothered than PoW and it have more applicability to practice than PoW
Delegated proof of stake
Time by time, we have some need for Blockchain network that need to be fast and cheap. Delegated proof of stake is one of those solution for this case.
Thanks for a limited number of validators, total maintain network fees now become more cheaper than any above architect, now can have block reward even you don’t maintain network through mechanism Delegate.
How is it work? Firstly, you have free native token and want to it increase in number. You stake it, then you have stake power. Now, you can use this power to choose one of two ways: Delegator or Candidate. If you choose Candidate you need to have some of your voting power and the top (e.g., 21) of the highest voting Candidates can become Validators, else you need is a node to maintain network maintenance. If you choose Delegator, then you can choose any Candidate in list, if they become Validators, they can share some percent of their block reward depends on their setting to share it with you. The problem if you become a Validator is you can be slashing your vote power (both of you and your Delegators), so it would be a strategy game of Delegators to choosing a Candidate that can be trust and have much benefit and can become Validator.
Compare with two others “proof of” above, it is fewer validators to maintain the network but the rule more stick with validators so they would have a financial loss if they cannot follow the network rule that be verified by others validators.
Proof of history
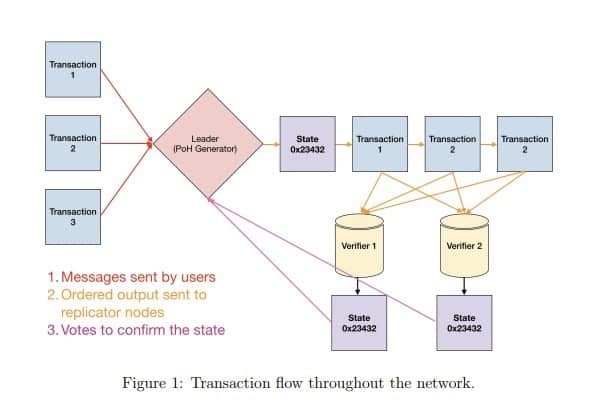
The last one I want to talk about is Proof of history that Solana used to make thing different.
In this algorithm, each transaction will have timestamp and state and verifier has role to make sure it is possible. This mechanism is much better as the verifier can choose up to 25 verifiers and each verifiers verify transaction can be working async so it would be much optimized about the power than others “proof of” (others “proof of” can verify only one transaction each time).
How block reward verifier? Well, it still based on Proof of stake to choosing who can get block reward.